Count Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) using the Cellometer Auto 2000
An Alternative to Flow Cytometry! Cellometer Auto 2000 Offers Accurate and Reproducible Counting Of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC).
 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells are used to measure immunological functions. Assays include proliferation, cytotoxicity and cytokine production. The use of cryopreserved PBMCs is critical both in clinical trials and biomedical research. In cancer immunotherapy, leukapheresis is often used to isolate immune system cells from a patient’s blood. Cells are then expanded or exposed to different agents depending on the vaccine design. Active cells are then infused back to the patient. Cell concentration and viability are essential parameters to monitor throughout the manufacturing process. Ficoll is routinely used to isolate mononuclear cells from bone marrow, peripheral blood, and umbilical cord blood. Monocytes and lymphocytes form a buffy coat under a layer of plasma. Cells are collected and washed. Typically, some residual platelets or red blood cells are mixed in the mononuclear cells. The functional assays on cryopreserved PBMC are associated with viability of the cells. Viability thresholds should be used in clinical trials in order to obtain reliable results of functional assays.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells are used to measure immunological functions. Assays include proliferation, cytotoxicity and cytokine production. The use of cryopreserved PBMCs is critical both in clinical trials and biomedical research. In cancer immunotherapy, leukapheresis is often used to isolate immune system cells from a patient’s blood. Cells are then expanded or exposed to different agents depending on the vaccine design. Active cells are then infused back to the patient. Cell concentration and viability are essential parameters to monitor throughout the manufacturing process. Ficoll is routinely used to isolate mononuclear cells from bone marrow, peripheral blood, and umbilical cord blood. Monocytes and lymphocytes form a buffy coat under a layer of plasma. Cells are collected and washed. Typically, some residual platelets or red blood cells are mixed in the mononuclear cells. The functional assays on cryopreserved PBMC are associated with viability of the cells. Viability thresholds should be used in clinical trials in order to obtain reliable results of functional assays.
Characteristics of PBMC experiments
- Cell quality degrades with time
- Large number of samples typically associated with clinical trials
- Cell sample are not pure, separation quality depends on patient sample and operator
Live PBMC concentration and viability are routinely measured for cell speration, processing and cryopreservation
- Label magnetic beads for cell separation
- Antibody labeling and staining for fluorescent active cell sorting and analysis
- Cryopreservation before adding cryo-cocktail
- Quality control after thawing
Challenges
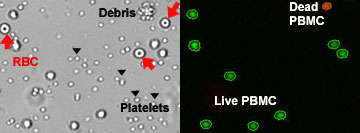
Image-based cell counters rely on software to process cell images captured by a digital camera. Trypan blue stained cells appear fully dark in color while viable cells have a clear bright center. Software algorithms are able to identify the two populations to calculate cell concentration and % viability. Mononuclear cells mixed with platelets or red blood cells can interfere with the accurate identification of the live cells or trypan blue stained dead cells. Additional steps including lysing of the red blood cells are required to get accurate results with bright field counting of trypan blue stained cells. Optimization of cell size gating are also needed to avoid counting platelets.
Solution
Dual Fluorescence PBMC Concentration and Viability using Cellometer Auto 2000
The Acridine Orange/Propidium Iodide (AO/PI) viability assay is a rapid, highly linear, functuionally correlated assay that is superior to conventional viability measurement by trypan blue exlusion. (HPC viability measurement: trypan blue versus acridine orange and propidium iodide, K. Mascotti, J. McCullough, and S. R. Burger, Blood Components, Transfusion, Volume 40, June 2000)
- * Nuclear staining dyes to simply and accurately identify the live and dead mononuclear cells

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.